The Evidence Room
Educational Content Overview
🔥 How the Body Stores and Burns Fat
– The body **stores fat** when insulin is high (after eating sugar or carbs).
– The body **burns fat** when insulin is low (fasting periods or low-carb intake).
– Most people spend too much time in ‘fat-storing mode’ due to frequent eating and carb-heavy meals.
🍭 What Happens When You Eat Sugar?
– Consuming sugar raises blood glucose levels.
– The body releases insulin to help absorb this sugar.
– Limited sugar is used for energy or stored as glycogen in muscles and liver.
🧈 What Happens to Excess Sugar?
– Once glycogen stores are full, the liver converts excess sugar into fat through a process called lipogenesis.
– This fat is stored in fat cells, especially as visceral fat (around the organs).
⚠️ The Hidden Dangers of Sugar
– Sugar consumption can silently trigger metabolic disorders.
– It can lead to insulin resistance, where cells stop responding to insulin.
– This raises the risk of:
• Type 2 diabetes
• Fatty liver disease
• Abdominal weight gain
• Heart disease
• Fatigue and brain fog
🍽️ Advice
– Stop blaming fat and calories alone.
– The key issue is understanding how sugar behaves in your body.
– Excess sugar is not just stored — it disrupts your entire metabolic health.
“TRY-B keeps your body nourished, stable, and gently in fat-burning mode — without the crashes, cravings, or embarrassing side effects of chemical pills.”
Injectable drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide are becoming popular for weight loss, but they carry real risks—especially for non-diabetic users. Here’s a comparison between these needle-based drugs and TRY-B.
1. Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are very common.
2. Pancreatitis and Gallbladder Issues
Increased risk of pancreatitis, gallstones, and gallbladder inflammation.
3. Rebound Weight Gain
Rapid regain of weight once treatment is stopped; doesn’t promote lasting habits.
4. Mental Health Effects
Potential increase in anxiety, depression, and disordered eating patterns.
5. Thyroid Tumors (Rare but Serious)
Linked to thyroid C-cell tumors in animal studies; carries black box warning.
6. Injection Site Risks
Risk of infection, skin irritation, or incorrect self-dosing.
7. Unknown Long-Term Effects
Limited safety data beyond 2 years of use in healthy individuals.
TRY-B A Safer Alternative, offers a non-invasive, food-based solution without synthetic hormones or pharmaceuticals. It nourishes the body with 27 nutrients, supports metabolism, and helps control appetite without side effects or medical intervention.

💊 What is Orlistat?
Orlistat (known by brand names like Xenical or Alli) is a weight-loss pill that works differently from slimming injections.
– It does **not suppress appetite** or affect hormones.
– Instead, it blocks an enzyme in the digestive system that breaks down fat.
– About **30% of the fat** you eat is not absorbed and instead exits the body through your stool.
⚙️ How It Works
– Orlistat works in the **intestines**, not in the brain or bloodstream.
– It prevents part of the dietary fat from being digested.
– That fat is then expelled — which is the cause of many of its side effects.
⚠️ Common & Uncomfortable Side Effects
– Oily or loose stools (steatorrhea)
– Urgent or uncontrollable bowel movements
– Gas with oily discharge
– Frequent trips to the bathroom
– Risk of **fat-soluble vitamin deficiency** (A, D, E, K)
– Stomach discomfort or cramps
– May cause **embarrassing social situations** due to leakage or accidents
Unlike chemical fat-blockers such as Orlistat, TRY-B works with your body — not against it. No embarrassing side effects, no risk of deficiencies. Just safe, elegant, science-backed nutrition for steady results.

🍭 What Happens When You Eat Sugar?
– Consuming sugar raises blood glucose levels. – The body releases insulin to help absorb this sugar. – Limited sugar is used for energy or stored as glycogen in muscles and liver.
🧈 What Happens to Excess Sugar?
– Once glycogen stores are full, the liver converts excess sugar into fat through a process called lipogenesis. – This fat is stored in fat cells, especially as visceral fat (around the organs).
⚠️ The Hidden Dangers of Sugar
– Sugar consumption can silently trigger metabolic disorders. – It can lead to insulin resistance, where cells stop responding to insulin. – This raises the risk of: • Type 2 diabetes • Fatty liver disease • Abdominal weight gain • Heart disease • Fatigue and brain fog
🍽️ Advice
– Stop blaming fat and calories alone. – The key issue is understanding how sugar behaves in your body. – Excess sugar is not just stored — it disrupts your entire metabolic health.
TRY-B keeps your body nourished, stable, and gently in fat-burning mode — without the crashes, cravings, or embarrassing side effects of chemical pills.

Water is life. Every cell, organ, and system in your body depends on it. But how much do you truly need each day to stay in balance?
General Daily Needs
• Women: about 2.7 liters (≈ 9 cups) • Men: about 3.7 liters (≈ 13 cups) Includes water from all fluids and food.
You May Need More If…
• You live in a hot climate • You’re physically active • You follow a low-carb, high-protein, or high-fiber diet • You’re pregnant or breastfeeding • You are sick or take medications that increase fluid loss
The Easy Rule
✅ Drink enough so that your urine is pale yellow — not dark, not completely clear.
Personalized Formula
💡 Multiply your body weight (in kg) by 30–35 ml to estimate your ideal daily water intake. Example: 70 kg × 30–35 ml = 2.1L to 2.5L per day
Sources & References
- U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2005). Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate.
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) – Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for water (2010).
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Water requirements, impinging factors, and recommended intakes (2005).
- Mayo Clinic – ‘How much water do you need every day?’ (2023).
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health – The Nutrition Source: Water.
- Clinical practice and sports medicine hydration guidelines (ACSM, ISSN).

1. Gastrointestinal Distress
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. These affect over 50% of users of GLP-1 agonists (like Ozempic or Wegovy), especially during dose titration.
📚 Source: JAMA Internal Medicine (2024) – [jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2816062]
2. Acute Pancreatitis
Cases of inflammation of the pancreas have been reported, some fatal. As of 2023, over 380 cases were reported to the UK’s MHRA.
📚 Source: Harvard Health Publishing – [health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/glp-1-diabetes-and-weight-loss-drug-side-effects-ozempic-face-and-more]
3. Metabolic & Endocrine Concerns
Risks include gallstones, thyroid tumors (observed in rodents), reduced kidney function, and gastric paralysis (gastroparesis). Many patients regain the weight after stopping treatment.
📚 Source: Wikipedia (Semaglutide entry) – [en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semaglutide]
4. Mental Health Effects
Thousands of cases have been reported of psychiatric symptoms including anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation. UK authorities are reviewing 85 deaths linked to these drugs.
📚 Source: The Scottish Sun (April 2024) – [thescottishsun.co.uk/health/14693350/warning-fat-jabs-depression-suicide]
5. Other Physical Effects
Known issues include ‘Ozempic face’ (facial fat loss), hair thinning, vision problems, and potential dental complications such as increased decay.
📚 Source: Johns Hopkins University – [hub.jhu.edu/2024/01/11/ozempic-wegovy-weight-loss-drugs-pros-cons]
6. Risk from Contaminated or Illegal Versions
Online ‘skinny jabs’ have caused life-threatening complications: internal bleeding, abscesses, and gastric perforation.
📚 Source: The Sun UK (March 2024) – [thesun.co.uk/health/33838115/skinny-jab-bought-online-could-have-died]
7. Financial Burden
Pharmaceutical-grade GLP-1 drugs can cost thousands per year. This excludes lab work, side effect treatment, and the cost of regaining weight if stopped.
📚 Source: The Sun (2024) – [thesun.co.uk/tvandshowbiz/32719175/gemma-collins-fat-loss-injections-weight-loss]
8. Balancing Benefits vs Risks
Some studies show reduced cardiovascular risk in obese patients, but this does not outweigh the risks for general weight-loss use.
📚 Source: British Heart Foundation – [bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/news/behind-the-headlines/weight-loss-injections]
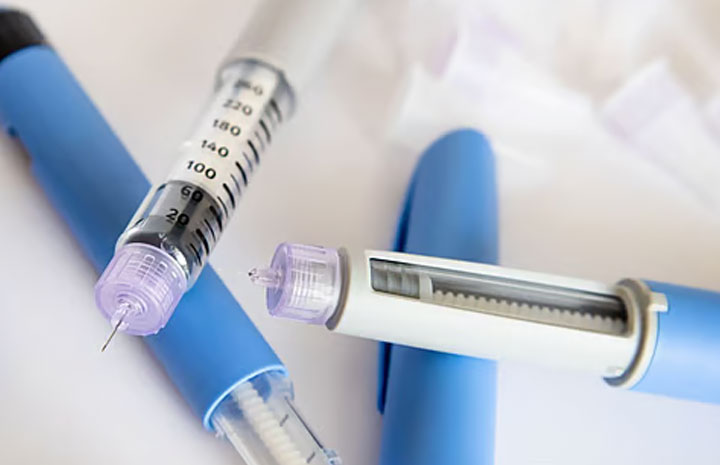
1. Gallbladder Disease & Gallstones
Use of GLP-1 receptor agonists has been linked to gallbladder disease, including gallstones and cholecystitis, particularly with long-term use.
📚 Source: MDPI Meta-analysis (2023) – https://www.mdpi.com/2813-0618/3/4/25
📚 Source: GoodRx – https://www.goodrx.com/wegovy/long-term-side-effects
2. Thyroid Cell Changes & Cancer Monitoring
FDA issued a boxed warning for potential risk of medullary thyroid carcinoma based on rodent studies. Human evidence remains inconclusive but under review.
📚 Source: PMC Study Review – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11202033
3. Kidney Injury & Stones
GLP-1 medications may cause dehydration-induced acute kidney injury and increase the risk of kidney stones.
📚 Source: MDPI Meta-analysis – https://www.mdpi.com/2813-0618/3/4/25
📚 Source: Nature Medicine Review (via Wikipedia) – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GLP-1_receptor_agonist
4. Gastroparesis & GI Stasis
Delayed gastric emptying can cause bloating, nausea, and rare cases of bowel obstruction. Estimated risk of 0.1%.
📚 Source: JAMA (2023) – https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2810542
📚 Source: Wikipedia – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semaglutide
5. Injection Site & Hypersensitivity Reactions
Reports of cellulitis, abscess formation, and rare anaphylaxis linked to long-term injection use.
📚 Source: MDPI Clinical Review – https://www.mdpi.com/2813-0618/3/4/25
6. Anesthesia Risk & Aspiration
GLP-1 medications slow gastric emptying, increasing aspiration risk under general anesthesia. Patients are advised to pause medication pre-surgery.
📚 Source: MDPI Surgical Safety Bulletin – https://www.mdpi.com/2813-0618/3/4/25
7. Eye & Vision Complications
Possible association with worsening or triggering age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) has been reported.
📚 Source: Wikipedia Clinical Summary – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semaglutide
8. Anti-Drug Antibodies & Efficacy Loss
Some patients may develop neutralizing antibodies, particularly with exenatide, which can reduce the drug’s effectiveness over time.
📚 Source: MDPI Immunogenicity Overview – https://www.mdpi.com/2813-0618/3/4/25



